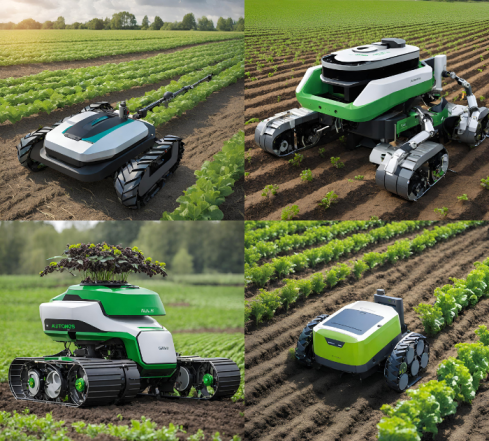
Weeding robots are the most creative invention in the agriculture field in recent times. A class of agricultural robots known as autonomous weeding robots can locate and eliminate weeds from crops without human intervention. These robots use a group of sensors, machine learning algorithms, and robotic arms to identify and remove weeds while avoiding damage to crops
These incredible machines can tell the difference between the plants we want to keep (crops) and the ones we don’t (weeds) by using smart cameras, special sensors, and clever technology like lidar. They’re like smart detectives in the field! They can move around different types of land and keep working even when the weather changes. This means they’re very helpful and reliable for farmers.
But that’s not all! These robots are like data collectors, too. As they do their job, they collect important information about how the soil is, how healthy the plants are, and how many weeds there are. This information helps farmers to take care of their fields. Using these robots in farming is a big help because it solves some big problems. One problem is that there aren’t always enough people to do all the work on the farms. These robots can fill in and do some of the tasks. They also make farming more friendly to our environment because they can reduce the need for harmful chemicals. So, when farmers use these robots, they can grow more crops, spend less money, and do it all in a way that’s better for our planet.
Table of Contents
Some key points about autonomous weeding robot
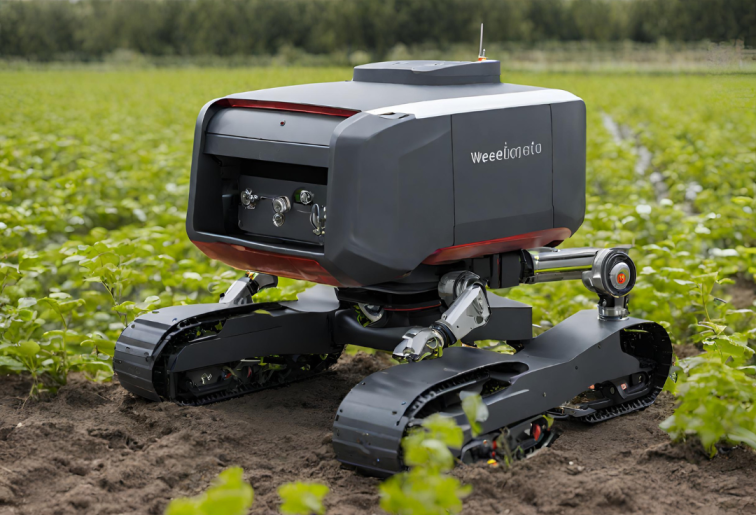

- Weed Detection: Autonomous weeding robots are equipped with sensors and computer vision technology to identify and differentiate between crops and weeds. They use cameras, lidar, or other sensors to scan the field and create a map of the area.
- Precision and Efficiency: These robots are designed to target and remove weeds with a high degree of precision. By selectively targeting weeds, they can reduce or eliminate the need for chemical herbicides and manual labor, making farming more environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
- Mechanical Weed Removal: Once a weed is identified, autonomous weeding robots use various mechanisms to remove it. This can include mechanical arms equipped with tools like robotic claws or rotating brushes to physically uproot or destroy the weed.
- Navigation and Control: These robots rely on advanced navigation systems and algorithms to move around the field autonomously. They can operate in various weather conditions and on different types of terrain.
- Data Collection: In addition to weed removal, these robots often collect data about the field, such as soil conditions, plant health, and weed density. This data can be used to make informed decisions about crop management.
- Integration with Farming Systems: Autonomous weeding robots can be integrated into existing farming systems and machinery. They can work alongside human operators or other automated farming equipment.
- Benefits: The use of autonomous weeding robots offers several benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, decreased reliance on chemical herbicides, and improved crop yields. They also help address labor shortages in agriculture, especially in regions where finding skilled labor is challenging.
- Challenges: Challenges in developing and deploying autonomous weeding robots include cost, technical complexity, and the need for robust software and AI algorithms to handle real-world conditions and varying weed types.
- Examples: Several companies and research institutions are working on autonomous weeding robot systems. Examples include the GreenBot from Fendt, the Oz robot from Roush, and various research projects at academic institutions worldwide.
How does this robot identify weeds?
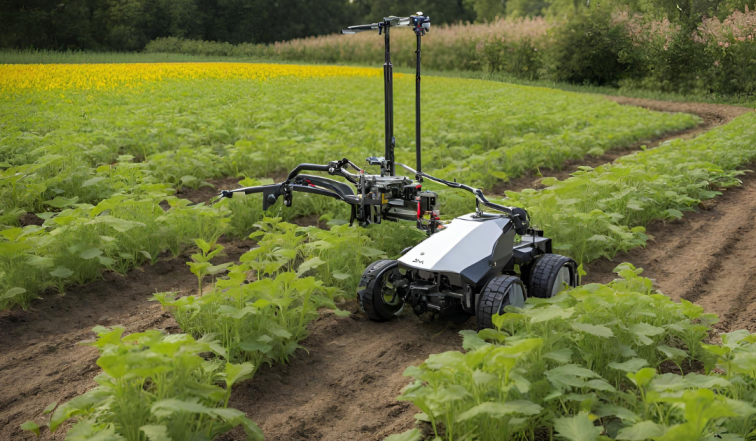

Autonomous weeding robots use a combination of sensors and machine learning algorithms to identify weeds. The sensors can detect the presence of plants and distinguish between crops and weeds based on their size, shape, and color. The machine learning algorithms then use this information to identify the weeds and determine the best way to remove them without damaging the crops.
How do these robots remove weeds?
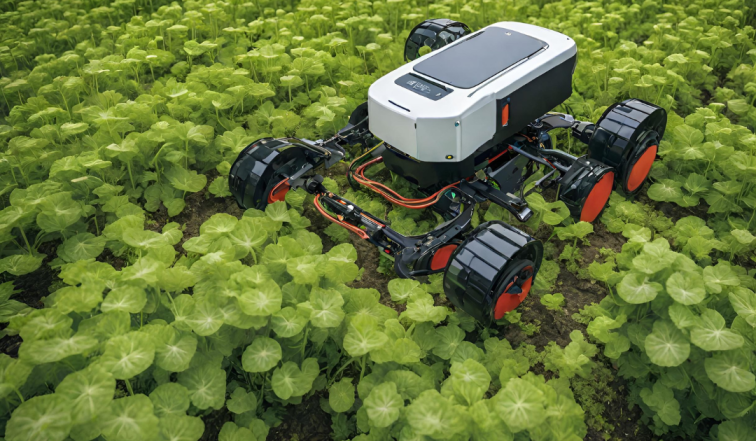

Autonomous weeding robots use a combination of sensors and machine learning algorithms to identify weeds. Based on their size, shape, and color, the sensors can identify the existence of plants and distinguish between crops and weeds. This data is then used by the machine learning algorithms to detect the weeds and decide how to remove them without harming the crops.
There are several ways that these robots can remove weeds. Some robots use a mechanical arm to pull the weed out of the ground, while others use a laser to burn the weed.
What are the benefits of using these robots?
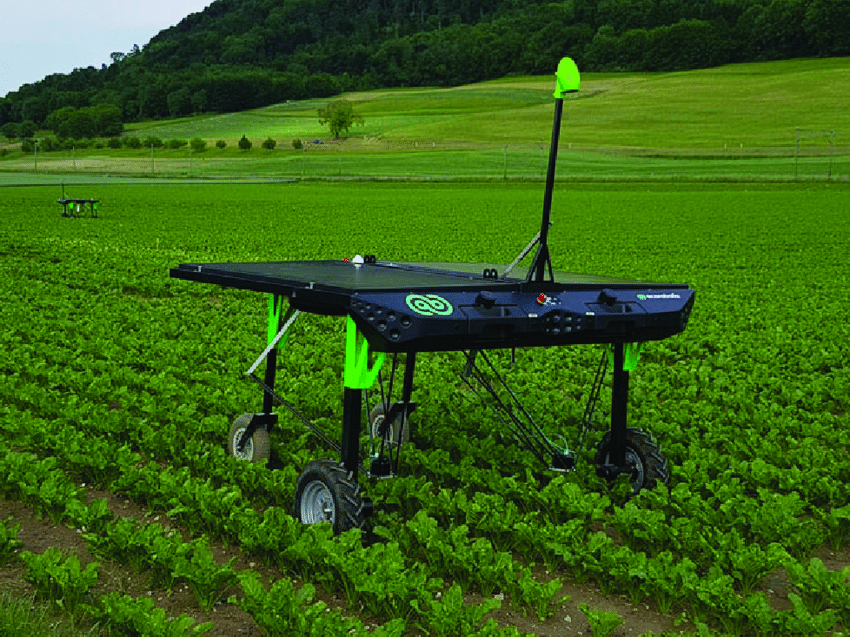

Using autonomous weeding robots in agriculture offers several benefits that contribute to more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective farming practices. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Precision Weed Removal: Autonomous weeding robots are equipped with advanced sensors and computer vision technology, allowing them to accurately identify and target weeds while avoiding damage to crops. This precision reduces the need for manual labor and minimizes the risk of accidentally harming valuable plants.
- Reduced Labor Costs: One of the most significant benefits is the reduction in labor costs. With the help of autonomous weeding robots, farmers can automate the labor-intensive task of weeding, reducing their dependency on human workers and potentially addressing labor shortages in the agricultural sector.
- Decreased Chemical Usage: By selectively removing weeds, these robots reduce their reliance on chemical herbicides. This contributes to environmentally friendly and sustainable farming practices, as it lowers the environmental impact of agriculture and reduces chemical runoff into water sources.
- Increased Crop Yields: Removing weeds efficiently allows crops to thrive without competition for resources like water, nutrients, and sunlight. As a result, crop yields tend to increase when using autonomous weeding robots.
- Improved Soil Health: Autonomous weeding robots can collect data about soil conditions as they operate in the field. This information helps farmers make informed decisions about soil management, leading to improved soil health and long-term sustainability.
- Data Collection and Insights: These robots are equipped with sensors that collect data on various aspects of the field, such as plant health, soil moisture, and weed density. Farmers can use this data to make data-driven decisions, optimize their farming practices, and respond to challenges promptly.
- Efficiency and 24/7 Operation: Autonomous robots can work day and night, in different weather conditions, and without rest. This continuous operation increases the efficiency of weed management and allows farmers to maximize their use of available resources.
- Environmental Benefits: By reducing the use of herbicides and promoting sustainable farming practices, autonomous weeding robots contribute to environmental conservation and protect biodiversity in agricultural ecosystems.
- Cost Savings: While there is an initial investment in acquiring and maintaining autonomous weeding robots, the long-term cost savings, including reduced labor and chemical costs, often outweigh the initial expenditure, making them a financially sound choice for many farmers.
- Labor Redistribution: By automating the weeding process, farmers can redirect labor resources to other essential tasks, such as planting, harvesting, and crop monitoring, which may require human expertise and decision-making.
Are there any disadvantages to using this robot?
While autonomous weeding robots offer numerous benefits, they also have some limitations and challenges that need to be considered.
1. Cost: The initial investment in autonomous weeding robots can be substantial. Acquiring and maintaining the technology, including sensors, cameras, and precision machinery, can be expensive for smaller farms, potentially limiting their adoption.
2. Complexity: Autonomous weeding robots are sophisticated machines that require advanced engineering and software development. This complexity can make them challenging to operate and maintain, necessitating skilled technicians for setup and troubleshooting.
3. Weed Detection Accuracy: While these robots are designed to accurately identify and remove weeds, their performance may vary depending on the type of crop, weed species, and environmental conditions. Achieving high levels of accuracy in all situations can be difficult.
4. Speed: Autonomous weeding robots may not work as quickly as human laborers, especially in large fields. Their speed can affect their efficiency in managing weed infestations, particularly in time-sensitive situations.
5. Limited Mobility: Some autonomous weeding robots may struggle with very uneven or steep terrain. They may also encounter challenges when navigating around obstacles like rocks or debris in the field.
6. Power Supply: Robots require a reliable power source, typically in the form of batteries or electrical connections. Ensuring uninterrupted power supply in remote or large agricultural areas can be challenging.
7. Adaptability to Crop Variability: Crop spacing, growth stages, and varieties can vary widely in agriculture. Autonomous weeding robots may need to be adapted or reprogrammed to accommodate these variations, which can be time-consuming.
8. Maintenance: Like any machinery, these robots require regular maintenance to ensure they function optimally. Dust, dirt, and wear and tear on mechanical components can lead to downtime and maintenance costs.
9. Data Handling and Analysis: The data collected by autonomous weeding robots must be managed and analyzed effectively to derive actionable insights. Farmers may need support in handling and interpreting this data.
10. Regulatory and Safety Concerns: Depending on the region and type of technology used, there may be regulatory hurdles and safety concerns related to the use of autonomous robots in agriculture.
11. Scalability: Adapting these robots to large-scale farming operations can be challenging. Multiple robots may be needed to cover large areas, and coordinating their actions effectively can be complex. 12. Limited Adaptation to New Weed Species: Autonomous weeding robots may have difficulty identifying and managing new or uncommon weed species that are not well documented in their programming.
Price
Hardware Price: $12,331.73With the support of artificial intelligence, weeds can be localized and burned with a laser beam. The laser is positioned using three motors with integrated control systems and three igus guide rails. The apparatus is fixed to a mobile robot that may roam the field by itself.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is an autonomous weeding robot, and how does it work?
- This question provides an introduction to the concept of autonomous weeding robots and their basic functioning, helping individuals understand the technology behind these robots.
- What types of sensors and technology do autonomous weeding robots use for weed detection?
- This question delves into the technical aspects of the robots, highlighting the sensors and technology that enable them to identify and differentiate between crops and weeds accurately.
- What are the benefits of using autonomous weeding robots in agriculture?
- This question focuses on the advantages of adopting this technology, including improved efficiency, reduced labor costs, and environmentally friendly farming practices.
- What are the limitations and challenges associated with autonomous weeding robots?
- This question addresses some of the potential drawbacks and challenges farmers may encounter when using these robots, offering a balanced perspective on their use.
- Are autonomous weeding robots compatible with different types of crops and farming practices?
- This question explores the adaptability of autonomous weeding robots to various crops, growth stages, and farming methods, helping farmers understand how to integrate this technology into their operations.