
Electric vehicles, also known as EVs, are the superheroes of modern vehicles. They do not use gas. EVs run on electricity. Just connect them with electricity, and they are ready to go. These modern vehicles change our thoughts about traditional vehicles. EVs do not use gas or emit CO, CO2 gases into the air, like our traditional cars. Instead, they help us breathe clean air and are a blessing for our planet. In this journey, we get to know more about EVs.
Table of Contents
The state and effect of Global Warming
Global warming is a critical environmental issue that has garnered increasing attention in recent years. It refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to the buildup of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The primary driver of global warming is the release of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases, mainly from human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
Global warming is when the Earth gets hotter because of gases in the air that trap heat. This happens because we use things like cars that produce these gases. Here’s what it does:
- Hotter Weather: Global warming makes the Earth warmer, causing really hot days. This is bad for farms, people, and animals.
- Melting Ice: The heat makes ice at the North and South Poles melt. When ice melts, it adds more water to the oceans, which makes them rise and flood coastal places.
- Higher Seas: The oceans are getting higher because of all the melted ice and because warm water takes up more space. This is scary for places near the ocean.
- Crazy Weather: Global warming leads to strange and dangerous weather, like hurricanes, droughts, floods, and big fires. These can hurt homes and people.
- Souring Oceans: The oceans are becoming more acidic because they soak up extra carbon dioxide. This hurts sea creatures like corals and shellfish.
- Loss of Wildlife: Many animals and plants can’t keep up with the changing climate, so they’re struggling to survive or even disappearing.
- Health Issues: Global warming can make the air dirty and spread diseases, making people sick.
- Money Problems: Dealing with the problems caused by global warming costs a lot of money, like fixing things after floods or dealing with crop failures.
To fix this, we need to use cleaner energy and be smarter about how we use energy. We also have to be ready for the changes that are already happening. It’s not just about the environment; it’s about working together to make the world better for everyone.
What Is Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles, or EVs for short, are like special cars that don’t need gasoline to run. Instead, they use electricity to power their engines. You can charge them by plugging them into a socket, just like your phone. Because they don’t burn gasoline, they don’t emit smelly fumes or pollution. EVs are great because they help keep the air clean and are super quiet. They’re like the future of cars, and they’re making our world a cleaner and quieter place to live.
Key Parts of Electric Vehicles
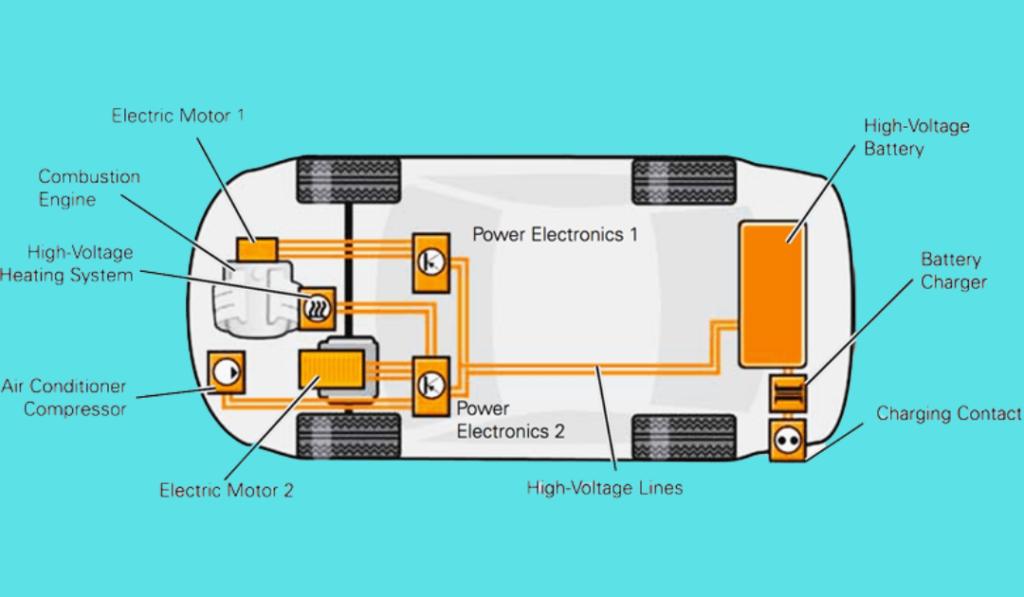
Electric vehicles (EVs) have several main parts that work together to provide clean and efficient transportation. The main components of an electric vehicle include:
- Electric Motor: The electric motor is the heart of an EV. It converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to drive the vehicle. Electric motors are known for their efficiency and instant torque.
- Battery Pack: The battery pack is a collection of individual lithium-ion cells that store electricity. It is the energy source for the electric motor and is rechargeable through charging ports.
- Charging Port: This is where the EV is connected to an external power source, like a home charging station or a public charging station, to recharge the battery.
- Power Electronics: Power electronics control the flow of electricity from the battery to the electric motor. They manage the voltage, current, and frequency of the electricity to ensure efficient power delivery.
- Onboard Charger: The onboard charger converts the alternating current (AC) from the charging source into direct current (DC) to charge the battery. It’s like the EV’s own mini charging station.
- Thermal Management System: EVs have a cooling and heating system to maintain the optimal temperature for the battery and other components. This helps extend the life of the battery and improve efficiency.
- Regenerative Braking System: This system captures energy during braking and deceleration, converting it back into electricity to recharge the battery. It enhances energy efficiency.
- Electric Vehicle Controller: The controller manages and regulates the power output of the electric motor, optimizing performance and efficiency.
- Transmission: Some EVs have a transmission to help control the power from the electric motor and provide different speeds or gears.
- Electric Vehicle Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS monitors the state of the battery, ensuring safe operation, extending battery life, and preventing overcharging or over discharging.
Which Features Make Them Unique From Traditional Cars
Electric vehicles (EVs) have several key features that make them stand out from traditional gasoline-powered cars:
- Zero Emissions: EVs produce no tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, which is great for the environment.
- Quiet Operation: Electric motors are super quiet, making EVs much quieter than traditional cars, contributing to reduced noise pollution.
- Energy Efficiency: EVs are highly energy-efficient, meaning they use a lot less energy to travel the same distance compared to gasoline cars, saving you money on fuel.
- Instant Torque: Electric motors provide instant torque, delivering quick acceleration and a smooth driving experience.
- Regenerative Braking: EVs can recover energy when braking, converting it back into electricity and improving energy efficiency.
- Low Maintenance: EVs have fewer moving parts, resulting in lower maintenance costs, as there’s no need for oil changes and fewer repairs.
- Reduced Operating Costs: Electricity is often cheaper than gasoline, leading to lower operating costs over the long term.
- Longer Range: Modern EVs have longer driving ranges, making them suitable for everyday use and longer trips.
- Charging Options: You can charge EVs at home with a regular outlet or use public charging stations, offering flexibility for recharging.
- Smart Features: Many EVs come with advanced technology and connectivity features, making them a part of the “smart” vehicle category.
- Environmental Benefits: By reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels, EVs contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable planet.
Advantages Of Electric Vehicles

Electric vehicles (EVs) have several main parts that work together to provide clean and efficient transportation. The main components of an electric vehicle include:
- Electric Motor: The electric motor is the heart of an EV. It converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to drive the vehicle. Electric motors are known for their efficiency and instant torque.
- Battery Pack: The battery pack is a collection of individual lithium-ion cells that store electricity. It is the energy source for the electric motor and is rechargeable through charging ports.
- Charging Port: This is where the EV is connected to an external power source, like a home charging station or a public charging station, to recharge the battery.
- Power Electronics: Power electronics control the flow of electricity from the battery to the electric motor. They manage the voltage, current, and frequency of the electricity to ensure efficient power delivery.
- Onboard Charger: The onboard charger converts the alternating current (AC) from the charging source into direct current (DC) to charge the battery. It’s like the EV’s own mini charging station.
- Thermal Management System: EVs have a cooling and heating system to maintain the optimal temperature for the battery and other components. This helps extend the life of the battery and improve efficiency.
- Regenerative Braking System: This system captures energy during braking and deceleration, converting it back into electricity to recharge the battery. It enhances energy efficiency.
- Electric Vehicle Controller: The controller manages and regulates the power output of the electric motor, optimizing performance and efficiency.
- Transmission: Some EVs have a transmission to help control the power from the electric motor and provide different speeds or gears.
- Electric Vehicle Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS monitors the state of the battery, ensuring safe operation, extending battery life, and preventing overcharging or over-discharging.
Disadvantages Of Electric Vehicles
While electric vehicles (EVs) offer several benefits, they also come with certain disadvantages that potential buyers should consider:
- Limited Range: Many EVs have a limited driving range on a single charge compared to gasoline vehicles. This can be a concern for long-distance travel, although ranges are improving with newer models.
- Charging Infrastructure: The availability of charging stations may be limited in some regions, making it challenging for EV owners to find convenient charging locations, particularly in rural areas.
- Charging Time: Charging an EV takes longer than refueling a gasoline vehicle. While home charging is convenient, public fast-charging stations are needed for quick top-ups during long trips.
- Upfront Cost: Electric vehicles often have a higher initial purchase price than comparable gasoline vehicles, mainly due to the cost of the battery. However, this cost is gradually decreasing as technology advances.
- Depreciation: EVs can depreciate faster than traditional vehicles, which may affect their resale value. However, this is changing as EVs become more popular.
- Limited Model Variety: Although the selection of EV models is increasing, it is still more limited compared to traditional vehicles, with fewer options in some vehicle classes.
- Charging Infrastructure Compatibility: Different EV models may use varying types of charging connectors, making it important to ensure compatibility with charging stations.
- Electricity Source: The environmental benefits of EVs depend on the source of the electricity used for charging. In regions with a high reliance on fossil fuels for electricity generation, the emissions savings may be reduced.
- Range Anxiety: Some drivers may experience “range anxiety,” a fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station. This anxiety can impact long journeys or unfamiliar routes.
- Charging Station Availability: In certain locations, EV charging stations may be occupied or unavailable, leading to inconveniences for EV owners.
- Battery Degradation: Over time, the battery’s capacity can degrade, reducing the driving range. However, this issue is gradually being addressed with improved battery technology.
- Limited Used EV Market: The used EV market is still developing, and potential buyers may have fewer options when compared to used gasoline vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How far can an electric vehicle go on a single charge?
- The driving range of an electric vehicle varies depending on the model. Most modern EVs can travel between 100 to 300 miles on a single charge. Some premium models offer even greater ranges. The actual range can also be influenced by factors such as driving habits, weather conditions, and vehicle age.
- How long does it take to charge an electric vehicle?
- Charging times depend on the charging infrastructure and the battery’s capacity. Home charging using a standard 120-volt outlet (Level 1) can take several hours or overnight. Level 2 chargers, which are faster and use 240 volts, typically take 4-8 hours. Fast-charging stations (Level 3 or DC fast chargers) can provide a significant charge in as little as 30 minutes, but not all vehicles are compatible with fast charging.
- Are there government incentives for purchasing an electric vehicle?
- Yes, many governments offer incentives to promote EV adoption. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, or discounts on the purchase price of the vehicle. Inquire with your local government to learn about the specific incentives available in your area.
- What about maintenance costs for electric vehicles?
- EVs generally have lower maintenance costs compared to traditional vehicles because they have fewer moving parts. You won’t need oil changes, and there’s less wear and tear on components like brakes. This can result in savings over the long term.
- Can I charge my electric vehicle at home?
- Yes, you can charge your EV at home if you have a dedicated charging station or access to a regular household outlet. Most EV owners use Level 2 charging stations, which provide faster charging times and can be installed in garages or near parking spaces.































I went over this website and I believe you have a lot of superb information, bookmarked (:.